AI Industries in China:
National Policies & Three Major Cities’ Competition for Foreign Investment†
Table of Contents
- National Policies for the Development of AI Industries in China
- Main Characteristics of the Development of AI Industries in Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Shanghai
- Conclusion
Estimated Reading Time
- 15.3 min
ChatGPT has taken the world by storm since it was introduced in November 2022. To compete with the new chatbot and similar artificial intelligence products for market share, Baidu launched ERNIE Bot in March 2023.1 While Baidu may appear to simply be following ChatGPT’s lead, ERNIE, the large model behind ERNIE Bot, had in fact already been recognized as early as 2019 by GLUE (General Language Understanding Evaluation), the authoritative collection of datasets used to evaluate NLU (natural language understanding) models.2
How far ERNIE Bot and other artificial intelligence industries (“AI industries”) will be able to develop in China depends on Chinese policies and legislation in the area. China has been actively planning for the development of AI industries since 2021, with its announcement of related national policies. Three major Chinese cities—Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Shanghai—have taken the lead to formulate their own local regulations in accordance with these policies. Each city has been working to develop AI industries in its own special way to attract foreign investment. What are the characteristics of each city’s development of this burgeoning sector?
National Policies for the Development of AI Industries in China
“AI industries were identified in [China’s] 14th Five-Year Plan for the National Economic and Social Development […] as among the core industries driving China’s digital economy.”
In March 2021, AI industries were identified in the Outline of the People’s Republic of China on the 14th Five-Year Plan for the National Economic and Social Development and on Long-Range Objectives for 2035 as among the core industries driving China’s digital economy.3 In December of the same year, the State Council issued the “14th Five-Year” Digital Economy Development Plan, which proposes a series of “development goals” and specific tasks regarding the digital economy:4
By 2025, the digital economy will enter a period of comprehensive expansion, and the added value of the core industries of the digital economy will account for 10% of GDP, […].
[Specific tasks include:]
Enhance the capability to innovate key technologies [by] aiming at strategic and forward-looking fields such as sensors, quantum information, network communications, integrated circuits, key software, big data, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and new materials, […].
Accelerate the digitalization of trade, […by] increasing the opening up of the service industry; exploring the relaxation of access to new formats of the digital economy; welcoming multinational companies in the global service industry to set up operations headquarters, research and development as well as design centers, procurement logistics centers, and settlement centers in China; actively introducing high-quality foreign-funded enterprises and entrepreneurial teams; and strengthening [the effort] to “bring in” international innovation resources.
[emphasis added]
In order to strengthen the coordination of efforts devoted to the development goals and specific tasks proposed in the “14th Five-Year” Digital Economy Development Plan, the State Council agreed in July 2022 to establish an “inter-ministerial joint meeting system for the development of the digital economy.” Led by the National Development and Reform Commission, the joint meeting is composed of 20 offices/ministries, including the Commission itself, the Office of the Cybersecurity and Informatization Commission of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, the Ministry of Education, the Ministry of Science and Technology, and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. The main responsibilities of the joint meeting are, inter alia, to “promote the implementation of strategies for the development of the digital economy”, “coordinate the formulation” of relevant policies, and “coordinate the promotion of major projects and pilot demonstrations of the digital economy”. The establishment of the joint meeting system marks an important step taken by China to integrate resources at the national level to vigorously develop the digital economy, of which AI industries are a central part.5
Main Characteristics of the Development of AI Industries in Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Shanghai
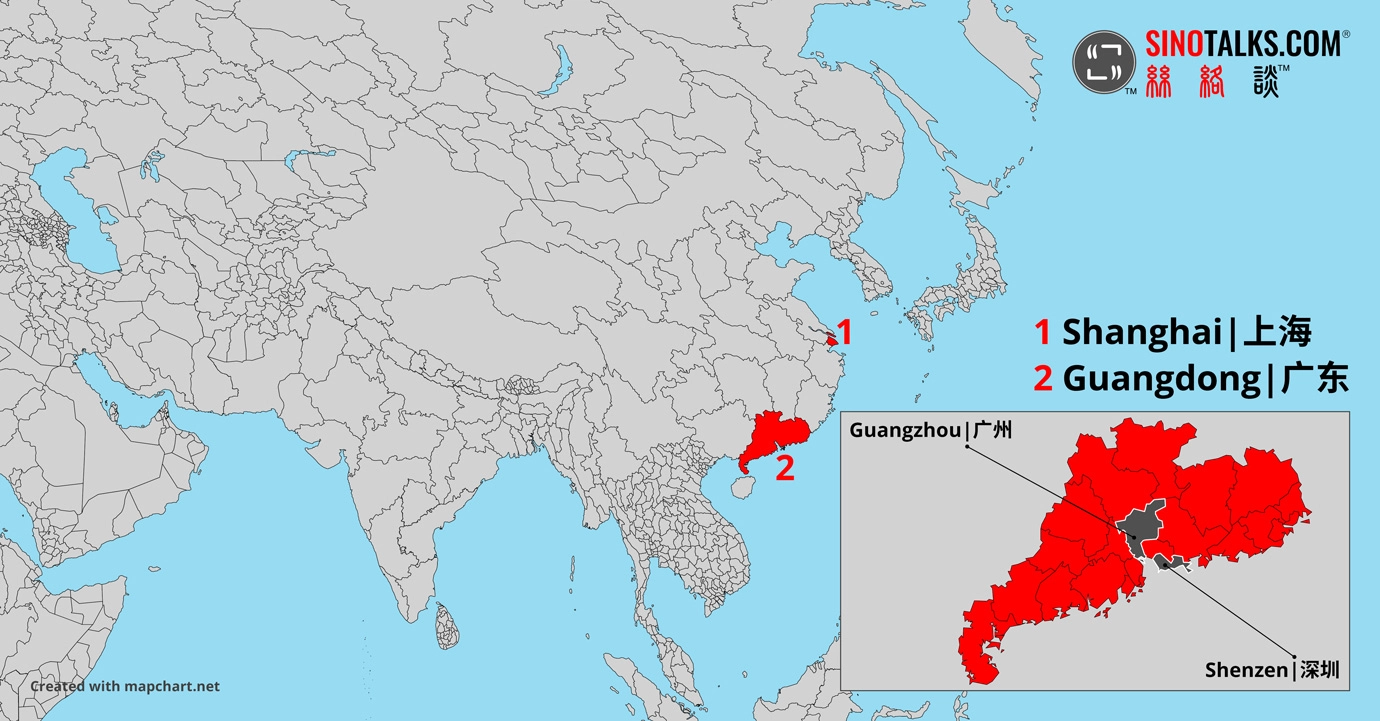
As China’s central government has gradually laid out clearer strategies regarding AI industries, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Shanghai have successively introduced related local regulations and policies promoting foreign investment, in the hope of establishing their firm footing in this fiercely competitive area.
In June 2022, the Regulation of Guangzhou City on Promoting the Digital Economy came into effect after it was approved by the Standing Committee of the People’s Congress of Guangdong Province. Being China’s first city-level regulation on the digital economy, the local legislation has, in total, 89 articles, of which eight are related to artificial intelligence.6 In August of the same year, the Standing Committee of the People’s Congress of Shenzhen City passed the Regulation of the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Promoting Artificial Intelligence Industries, China’s first piece of legislation focusing specifically on AI industries.7 A month later, in September 2022, the Standing Committee of the People’s Congress of Shanghai Municipality, which, like three other municipalities in China, i.e., Beijing, Chongqing, and Tianjin, has provincial status, passed the Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Promoting the Development of Artificial Intelligence Industries, China’s first piece of provincial-level legislation specifically concerning AI industries.8
Through the above-mentioned regulations and policies promoting foreign investment discussed below, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Shanghai have highlighted the special characteristics of their development of AI industries so as to attract foreign investment and, thereby, bolster their efforts in this increasingly important area.
- Guangzhou
Unlike the Regulation of the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Promoting Artificial Intelligence Industries9 and the Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Promoting the Development of Artificial Intelligence Industries,10 the Regulation of Guangzhou City on Promoting the Digital Economy covers not only artificial intelligence, but also the construction of digital infrastructure (e.g., information and communication networks, data centers, and edge computing nodes) and the provision of special facilities (e.g., databases for urban historical and cultural projects).11 Its more expansive content allows the Regulation of Guangzhou City on Promoting the Digital Economy to provide more comprehensive protection for investment in artificial intelligence.
According to the Overall Plan for the Construction of the Guangzhou Artificial Intelligence and Digital Economy Pilot Zone, Guangzhou’s key AI industries are those related to image and speech recognition, machine translation, virtual reality, and augmented reality.12
All these efforts seem to have contributed to Guangzhou’s being chosen as a desirable location for artificial intelligence enterprises. According to the 2022 Report on the Development of China’s Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Technology Industry, 8.55% of all artificial intelligence enterprises in China are located in Guangzhou. Compared with other major cities in the country, Guangzhou has the fourth highest percentage of such enterprises.13 This relatively high rank will likely influence foreign investors interested in AI industries to consider Guangzhou favorably.
- Shenzhen
In order to actively recruit top talent, the Regulation of the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Promoting Artificial Intelligence Industries emphasizes “the construction of key laboratories, special bases for experiments, […] and other innovation carriers”14 as well as “the conferment of the power to decide on technical routes and the power to use funds on artificial intelligence innovation teams and leading talent”.15 This focus of the Shenzhen legislation undoubtedly makes the city very attractive to foreign investors.
In addition, in September 2022, Shenzhen announced the Regulation of the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Foreign Investment,16 to, inter alia, note the city’s strict adherence to the national “negative list for foreign investment access”—which identifies fields prohibited or restricted from receiving foreign investment—and, therefore, prohibit any formulation of restrictive or prohibitive measures for foreign investment access outside this national list. For those fields that are not on the “negative list for foreign investment access” (e.g., AI industries), the Regulation makes it clear that both foreign investors and domestic enterprises are allowed to invest in them.17 Article 12 of the Regulation further injects a confidence boost to foreign investors of AI industries as it states that Shenzhen “encourages and guides foreign investors to invest in key development areas such as advanced manufacturing, emerging industries, high-tech, energy conservation and environmental protection [emphasis added]”.
The Action Plan of Shenzhen City for the Development of Next Generation Artificial Intelligence (2019-2023) notes that, among various artificial intelligence products, Shenzhen particularly supports the development of intelligent robots, intelligent drones, intelligent medical systems, intelligent connected vehicles, and intelligent transportation systems.18
According to the 2022 Report on the Development of China’s Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Technology Industry, 13.41% of all artificial intelligence enterprises in China are located in Shenzhen, making it the city with the second highest percentage of such enterprises in China.19
- Shanghai
In order to expand the space for the development of artificial intelligence, a major characteristic of the Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Promoting the Development of Artificial Intelligence Industries20 is to allow the exploration of a more flexible and tolerant governance model. For example, Article 65 states:
A list of minor violations of law occurring in the course of developing artificial intelligence industries may be formulated by the relevant department of the Municipality to legally exempt these violations from administrative penalties. Measures such as education through criticism and guidance interviews shall be taken to promote [the abilities of] citizens, legal persons, and other organizations to carry out production and business activities in accordance with laws and regulations.
In September 2020, the Standing Committee of the People’s Congress of Shanghai Municipality passed the Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Foreign Investment,21 the first foreign investment regulation to be issued by a local people’s congress since the coming into effect of the Foreign Investment Law of the People’s Republic of China.22 Like the Regulation of the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Foreign Investment,23 the Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Foreign Investment notes Shanghai’s strict adherence to the national “negative list for foreign investment access” and makes it clear that both foreign investors and domestic enterprises may invest in fields that are not on the list (e.g., AI industries).24 In addition, Article 20 of the Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Foreign Investment provides that Shanghai “encourages and guides foreign investors to invest in key development areas as stated in the national Catalogue of Encouraged Industries for Foreign Investment or as identified by the Municipality”, and includes a clear statement that foreign investors may enjoy special treatment—such as preferential taxation and land use—when investing in these areas.
Articles 40 to 45 of the Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Promoting the Development of Artificial Intelligence Industries list key products whose development Shanghai promotes: high-performance smart chips, artificial intelligence framework software, intelligent robots, intelligent connected vehicles, drones, and intelligent medical devices.25
According to the 2022 Report on the Development of China’s Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Technology Industry, 13.09% of all artificial intelligence enterprises in China are located in Shanghai, making it the city with the third highest percentage of such enterprises in the country.26
Conclusion
“The particular characteristics of each city’s development of AI industries can be seen through a review of the various aspects highlighted above […] and summarized in the table below.”
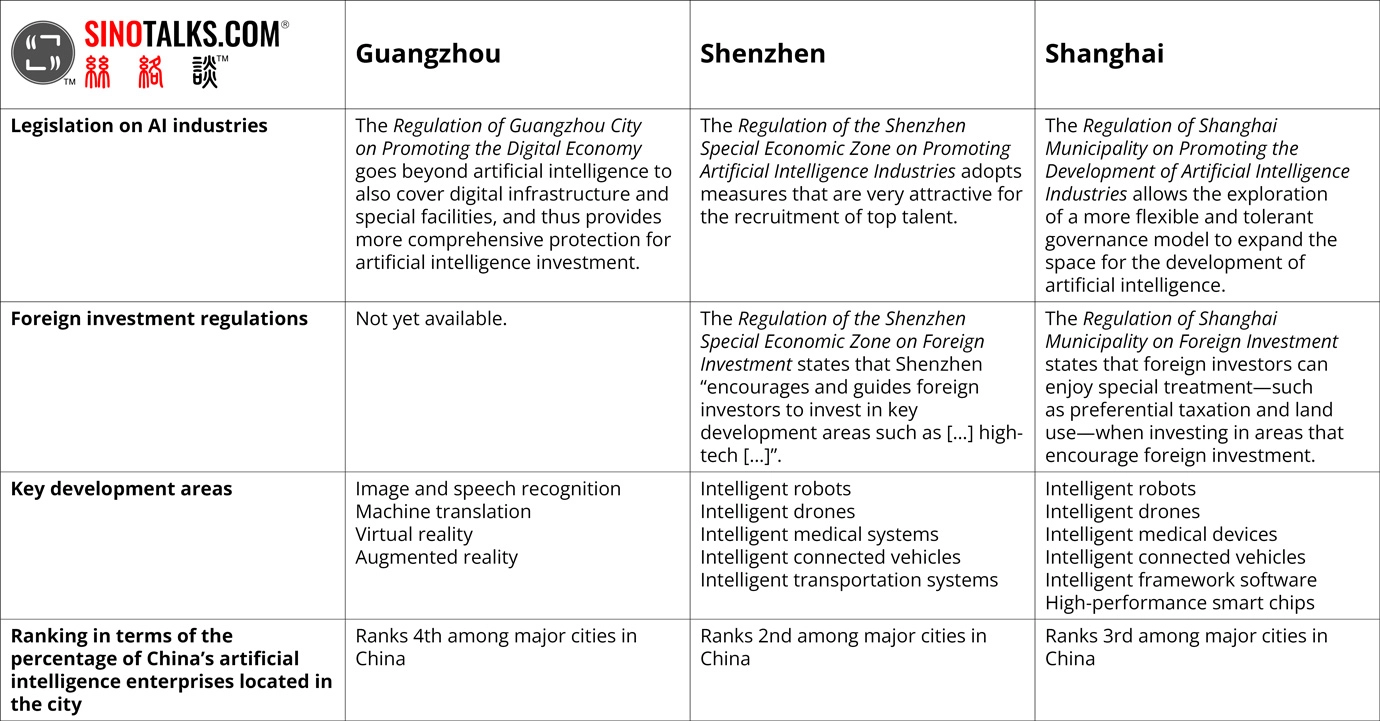
Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Shanghai have developed their AI industries in accordance with the guidance provided by national policies while focusing on specific areas in their locality. The particular characteristics of each city’s development of AI industries can be seen through a review of the various aspects highlighted above—legislation on AI industries, foreign investment regulations, key development areas, and ranking in terms of the percentage of China’s artificial intelligence enterprises located in the city—and summarized in the table below.
Table: Main Characteristics of Three Major Cities’ Development of AI Industries
When foreign investors choose to enter China’s artificial intelligence market through one of these three major cities, they should pursue their own strategic goals and core competitiveness by comprehensively considering the different paths and focuses of these cities’ development of local AI industries. Evaluating these along with other important factors—such as these cities’ talent resources, innovation atmosphere, market demand, and regional coordination—will allow these investors to seize AI-related opportunities available in the current climate and, more importantly, to begin establishing its footing in China’s digital economy, which is becoming increasingly important and central to life and business around the world.
† The citation of this article is: Peining Wang & Ruoyu Ren, AI Industries in China: National Policies & Three Major Cities’ Competition for Foreign Investment, SINOTALKS.COM®, SinoForum&Foresight™, May 30, 2023, https://sinotalks.com/sinoforumforesight/202305-wang-ren-ai-industries. The original, Chinese version of this article was edited by Dr. Mei Gechlik. The English version was prepared, with support from the authors, by members of the Editorial Board of SINOTALKS®, and was finalized by Jennifer Ingram, Nathan Harpainter, and Dr. Mei Gechlik. The information and views set out in this article are the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the work or views of SINOTALKS®.
1 Baidu Unveils ERNIE Bot, the Latest Generative AI Mastering Chinese Language and Multi-Modal Generation, PR Newswire, Mar. 16, 2023, https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/baidu-unveils-ernie-bot-the-latest-generative-ai-mastering-chinese-language-and-multi-modal-generation-301774240.html.
2 Baidu’s Pre-Training Model ERNIE Achieves New NLP Benchmark Record, Baidu Research, Dec. 11, 2019, http://research.baidu.com/Blog/index-view?id=128.
3《中华人民共和国国民经济和社会发展第十四个五年规划和2035年远景目标纲要》 (Outline of the People’s Republic of China on the 14th Five-Year Plan for the National Economic and Social Development and on Long-Range Objectives for 2035), issued on and effective as of Mar. 13, 2021, http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-03/13/content_5592681.htm.
4《国务院关于印发〈“十四五”数字经济发展规划〉的通知》 (Notice of the State Council on Printing and Distributing the “‘14th Five-Year’ Digital Economy Development Plan”), issued on and effective as of Dec. 12, 2021, http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2022-01/12/content_5667817.htm.
5《国务院办公厅关于同意建立数字经济发展部际联席会议制度的函》 (Letter of the General Office of the State Council on Agreeing to Establish an Inter-Ministerial Joint Meeting System for the Development of the Digital Economy), issued on and effective as of July 11, 2022, http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2022-07/25/content_5702717.htm.
6《广州市数字经济促进条例》 (Regulation of Guangzhou City on Promoting the Digital Economy), passed by the Standing Committee of the People’s Congress of Guangzhou City on Dec. 31, 2021, approved by the Standing Committee of the People’s Congress of Guangdong Province on Mar. 29, 2022, issued on Apr. 6, 2022, effective as of June 1, 2022, https://gzdaily.dayoo.com/pc/html/2022-04/13/content_879_789248.htm. The eight articles that refer to artificial intelligence are Articles 8, 11, 12, 14, 40, 55, 85, and 88.
7《深圳经济特区人工智能产业促进条例》 (Regulation of the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Promoting Artificial Intelligence Industries), passed by the Standing Committee of the People’s Congress of Shenzhen City on Aug. 30, 2022, issued on Sept. 5, 2022, effective as of Nov. 1, 2022, http://www.szrd.gov.cn/szrd_zlda/szrd_zlda_flfg/flfg_szfg/content/post_834707.html.
8《上海市促进人工智能产业发展条例》 (Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Promoting the Development of Artificial Intelligence Industries), passed and issued by the Standing Committee of the People’s Congress of Shanghai Municipality on Sept. 22, 2022, effective as of Oct. 1, 2022, https://www.ssme.sh.gov.cn/public/news!loadNewsDetail.do?id=2c91c28d83647d7001837da955a60a55.
9 Regulation of the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Promoting Artificial Intelligence Industries, supra note 7.
10 Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Promoting the Development of Artificial Intelligence Industries, supra note 8.
11 Regulation of Guangzhou City on Promoting the Digital Economy, supra note 6.
12《广东省推进粤港澳大湾区建设领导小组关于印发〈广州人工智能与数字经济试验区建设总体方案〉的通知》 (Notice of the Leading Group of Guangdong Province for Promoting the Construction of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area on Printing and Distributing the “Overall Plan for the Construction of the Guangzhou Artificial Intelligence and Digital Economy Pilot Zone”), issued on and effective as of Jan. 11, 2020, http://drc.gd.gov.cn/ywtz/content/post_2899440.html.
13 中国新一代人工智能发展战略研究院 (China Strategic Research Institute for the Development of Next Generation Artificial Intelligence), 《中国新一代人工智能科技产业发展报告2022》 (2022 Report on the Development of China’s Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Technology Industry), June 24, 2022, https://www.sohu.com/a/638516229_121637204 (hereinafter “2022 Report on the Development of China’s Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Technology Industry”).
14 Regulation of the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Promoting Artificial Intelligence Industries, supra note 7, Article 16.
15 Id. Article 25.
16《深圳经济特区外商投资条例》 (Regulation of the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Foreign Investment), passed by the Standing Committee of the People’s Congress of Shenzhen City on Aug. 30, 2022, issued on Sept. 5, 2022, effective as of Nov. 1, 2022, https://flk.npc.gov.cn/detail2.html?ZmY4MDgxODE4MzQ1ZmFkYTAxODM1NGRjNjAyYTE4YWE%3D.
17 Id. Articles 10 and 11.
18《深圳市人民政府关于印发〈深圳市新一代人工智能发展行动计划(2019-2023年)〉的通知》 (Notice of the People’s Government of Shenzhen City on Printing and Distributing the “Action Plan of Shenzhen City for the Development of Next Generation Artificial Intelligence (2019-2023)”), issued on and effective as of May 10, 2019, http://www.sz.gov.cn/zfgb/2019/gb1102/content/post_5017778.html.
19 2022 Report on the Development of China’s Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Technology Industry, supra note 13.
20 Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Promoting the Development of Artificial Intelligence Industries, supra note 8.
21《上海市外商投资条例》 (Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Foreign Investment), passed and issued by the Standing Committee of the People’s Congress of Shanghai Municipality on Sept. 25, 2020, effective as of Nov. 1, 2020, https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fggz/lywzjw/wstz/202011/t20201123_1251019.html.
22《中华人民共和国外商投资法》(Foreign Investment Law of the People’s Republic of China), passed and issued on Mar. 15, 2019, effective as of Jan. 1, 2020, http://tfs.mofcom.gov.cn/article/fl/202101/20210103034662.shtml.
23 Regulation of the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone on Foreign Investment, supra note 16.
24 Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Foreign Investment, supra note 21, Articles 4 and 40.
25 Regulation of Shanghai Municipality on Promoting the Development of Artificial Intelligence Industries, supra note 8.
26 2022 Report on the Development of China’s Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Technology Industry, supra note 13.





